The advantages of the impedance-controlled 4 MHz radiofrequency technology lie in its physics
Using the CURIS© 4 MHz radiofrequency generator energy is absorbed evenly inside the cells avoiding the energy to heat up the outer layer as it happens during conventional high frequency technology8. This even flow of energy inside the cells makes the CURIS© 4 MHz radiofrequency generator an optimal tool for both cutting and coagulation in precision electrosurgery.
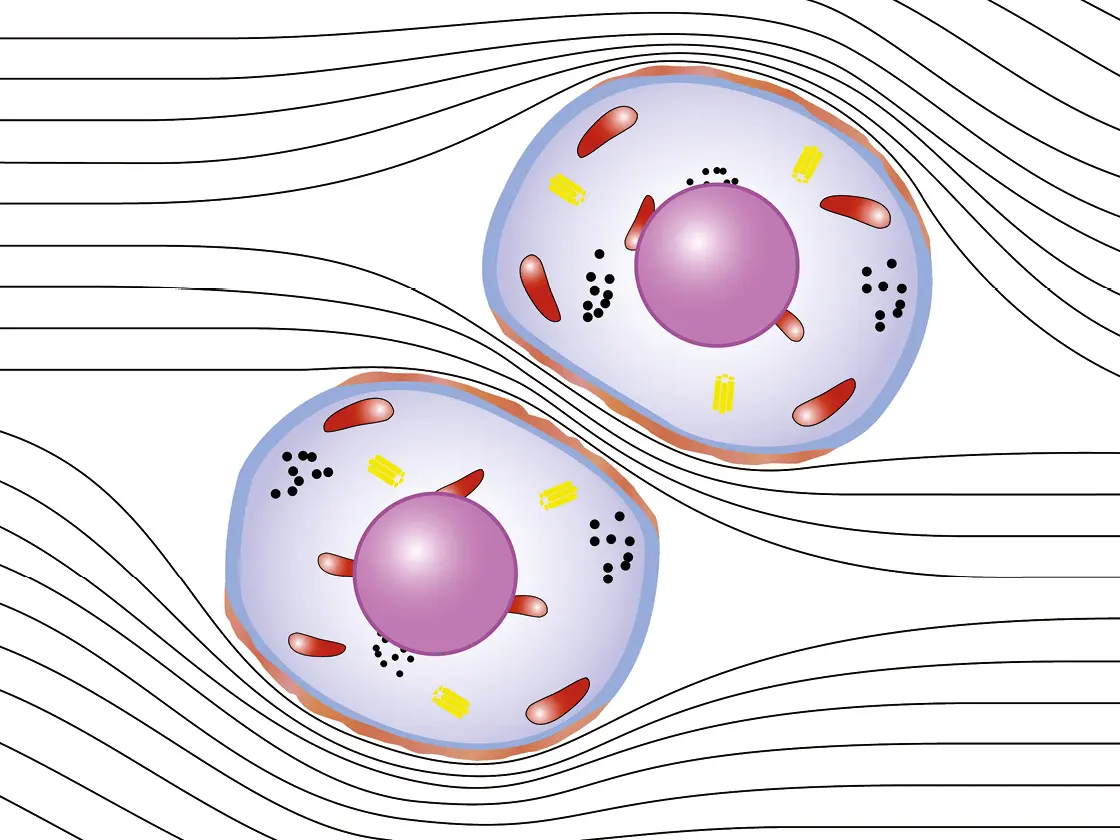
Conventional electrosurgical units
With conventional electrosurgical units, the electromagnetic field concentrates between the cells and heats up only the outer layer. Illustration only.
Fig. 1a
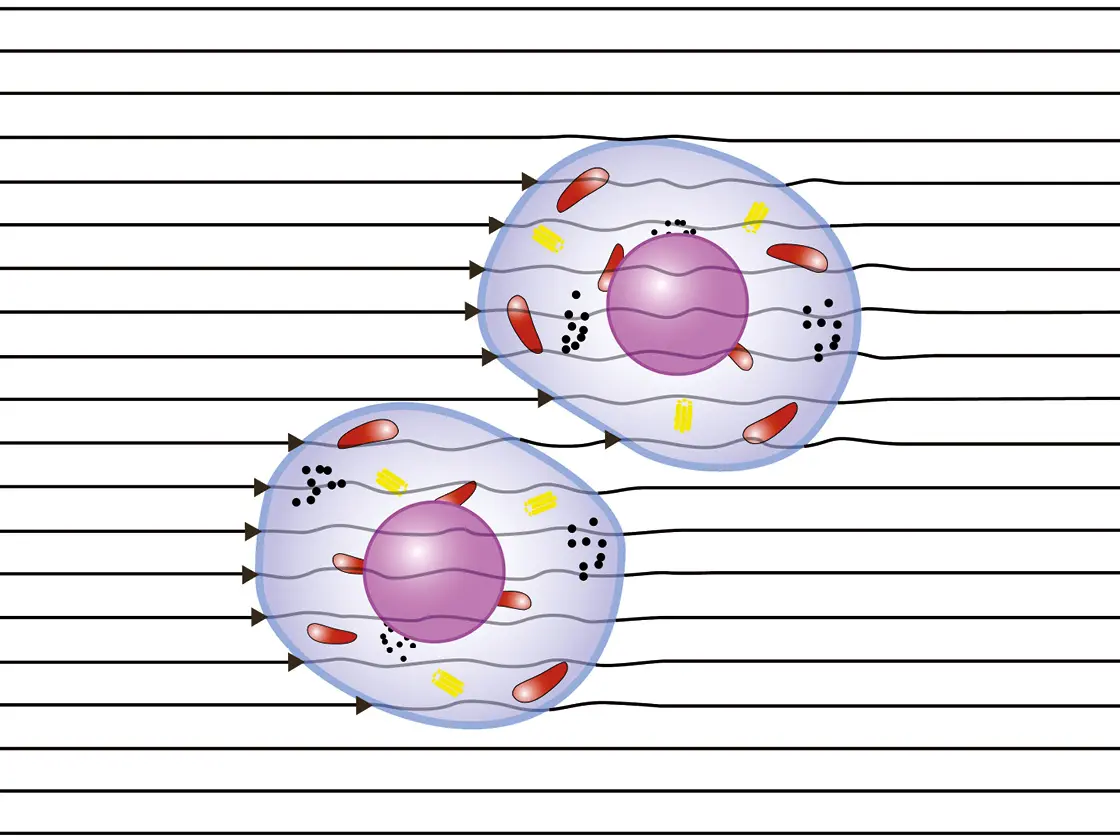
CURIS® 4 MHz Radiofrequency Generator
With the CURIS© 4 MHz radiofrequency generator, cell membranes are conductive and the energy is absorbed evenly inside the cells. The results are highly focussed tissue effects. Illustration only.
Fig. 1b
Better Wound Healing
A comparison of the healing process of lesions in albino rats created by different technologies showed proven benefits of the 4 MHz radiofrequency technology in terms of wound healing. Using the impedancecontrolled CURIS© 4 MHz radiofrequency generator turned out to be more targeted and precise compared to conventional high frequency, preserving the basal membrane as well as the deep layers of the epithelium, thus causing less profound wounds.6 The histological assessment also showed that wound healing using the CURIS© 4 MHz radiofrequency generator is faster compared to conventional high frequency. Radiofrequency induced wounds show complete epithelialization after seven days in contrast to the lesions produced by high frequency which show abundant inflammation associated with focal suppurations (see fig. 2).
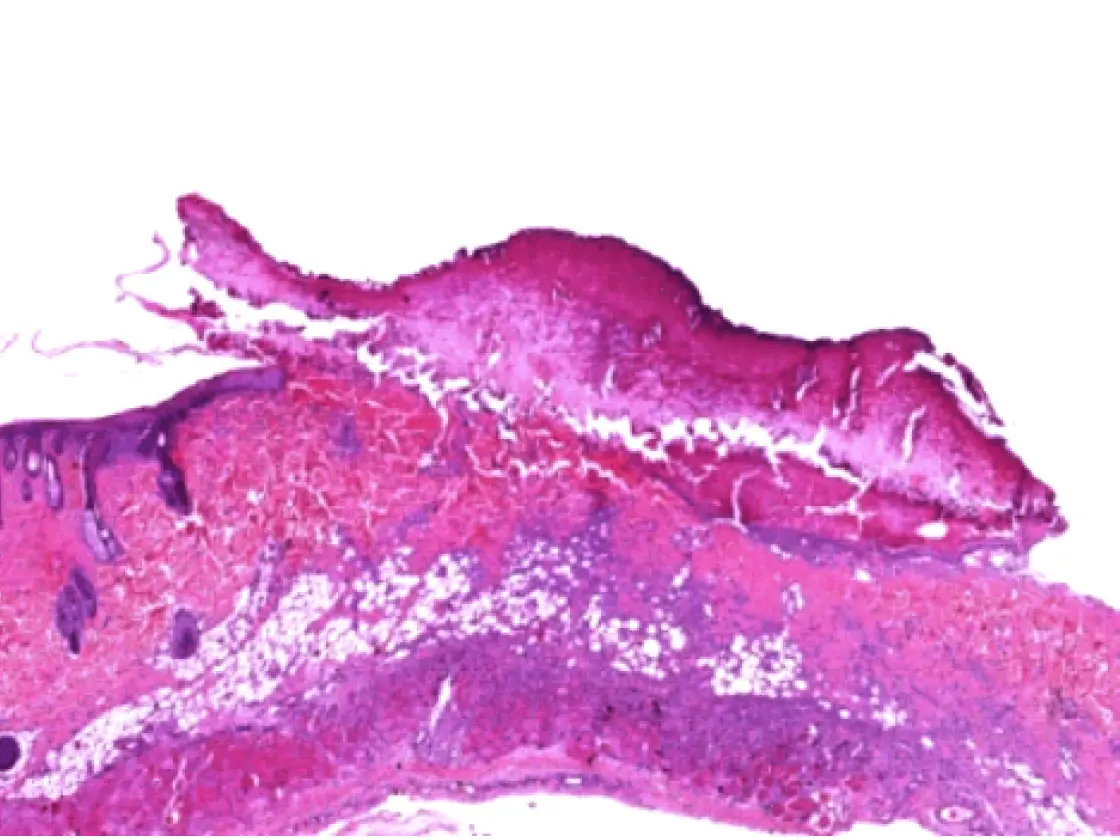
High frequency / electric cauterization
Histological aspects on day seven: comparing radiofrequency and conventional high frequency
Fig. 2
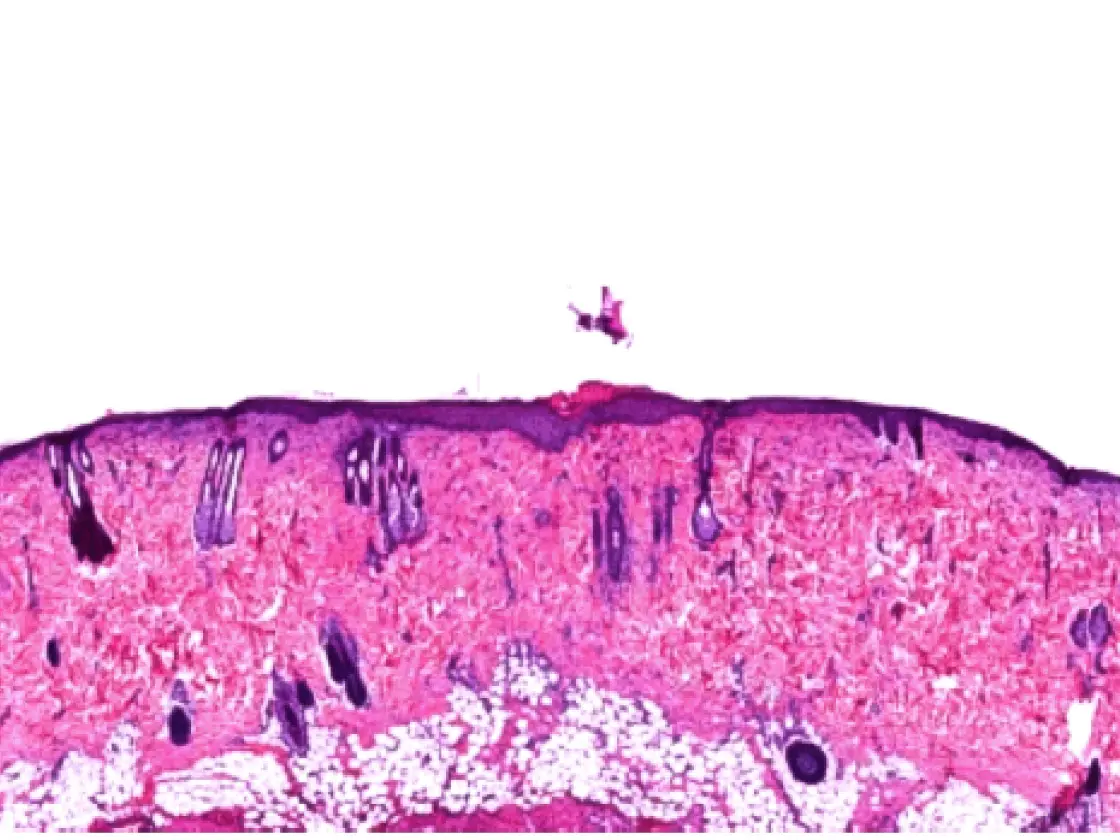
Radiofrequency
A study among 25 patients presenting with oral or oropharyngeal tumors showed that radiofrequency-assisted resected specimen using the CURIS© 4 MHz radiofrequency generator were better assessable than laser-assisted resected specimen. The impedance-controlled 4 MHz radiofrequency technology produced predominantly smooth resection margins and reduced the tissue resistance. Compared to CO2 laser and high frequency technology, the 4 MHz radiofrequency technology caused the narrowest lesions and coagulation zones.5
Minimal Lateral Thermal Damage
Further studies support the conclusion that the impedance-controlled 4 MHz radiofrequency technology produces less lateral thermal damage than other technologies:
It was shown that the CURIS 4 MHz radiofrequency generator achieved the best cutting width (see fig. 2), the smallest coagulation defects and the narrowest lesions at all energy levels compared to CO2 laser, YAG laser and high frequency technology. Moreover, it produced the smallest coagulation zone in different tissue types at various energy levels compared to the other technologies (see fig. 3a & 3b). Thus, the impedance-controlled 4 MHz radiofrequency technology preserves best the tumor-adjacent structures and improves pathological assessment.4
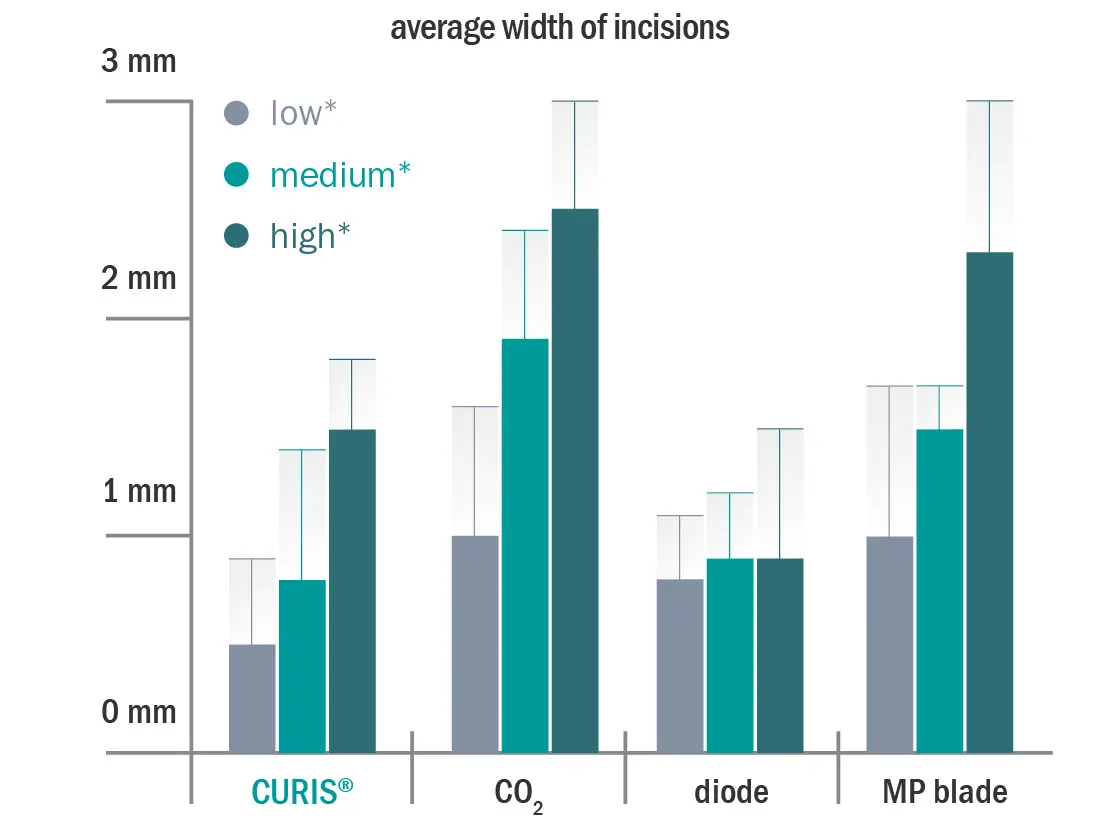
Comparing the average width of incisions produced by different instruments at different energy levels
Fig. 3
* Energy level
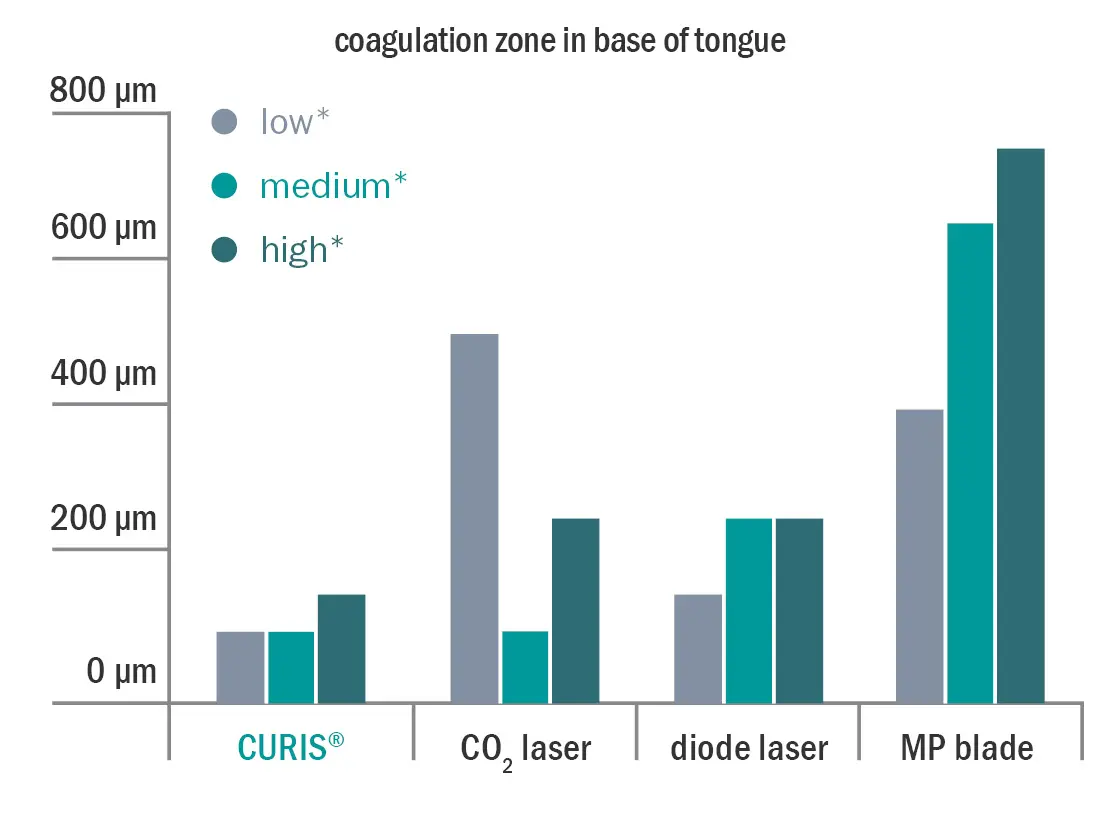
Comparing the coagulation zone of the instrument in the base of tongue at different energy levels
Fig. 3a
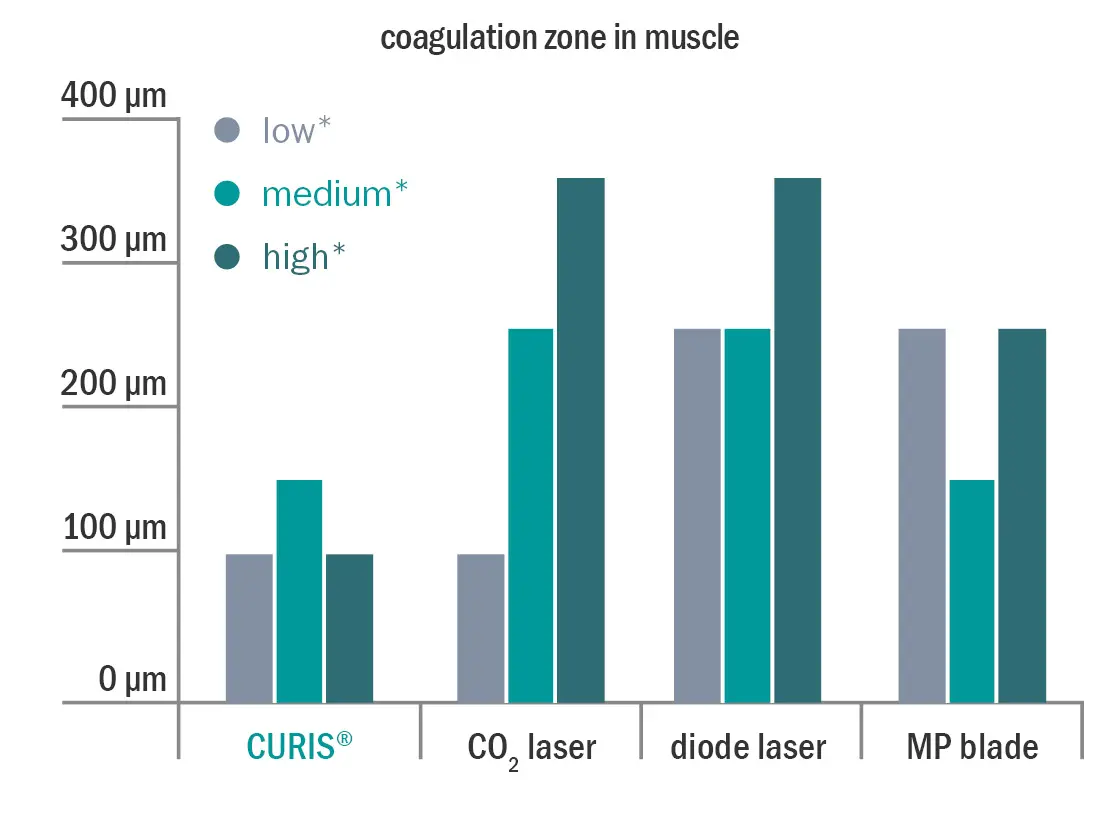
Comparing the coagulation zone of the instrument in muscle tissue at different energy levels
Fig. 3b
Precise Coagulation and Gentle Tissue Effects
The precision and quality of coagulation results can be observed in the effects on the tissue. A study comparing bipolar coagulations on egg yolk showed that the impedance-controlled CURIS© 4 MHz radiofrequency generator achieves gentler effects as well as more reproducible results compared to conventional high frequency. With each of the two generators, 100 coagulations were performed for 1, 2 and 3 seconds, respectively. The results were evaluated by three blinded analysts on a visual analog scale for three criteria: edge sharpness, homogeneity and shape of the coagulation (see fig. 5 & 6).9
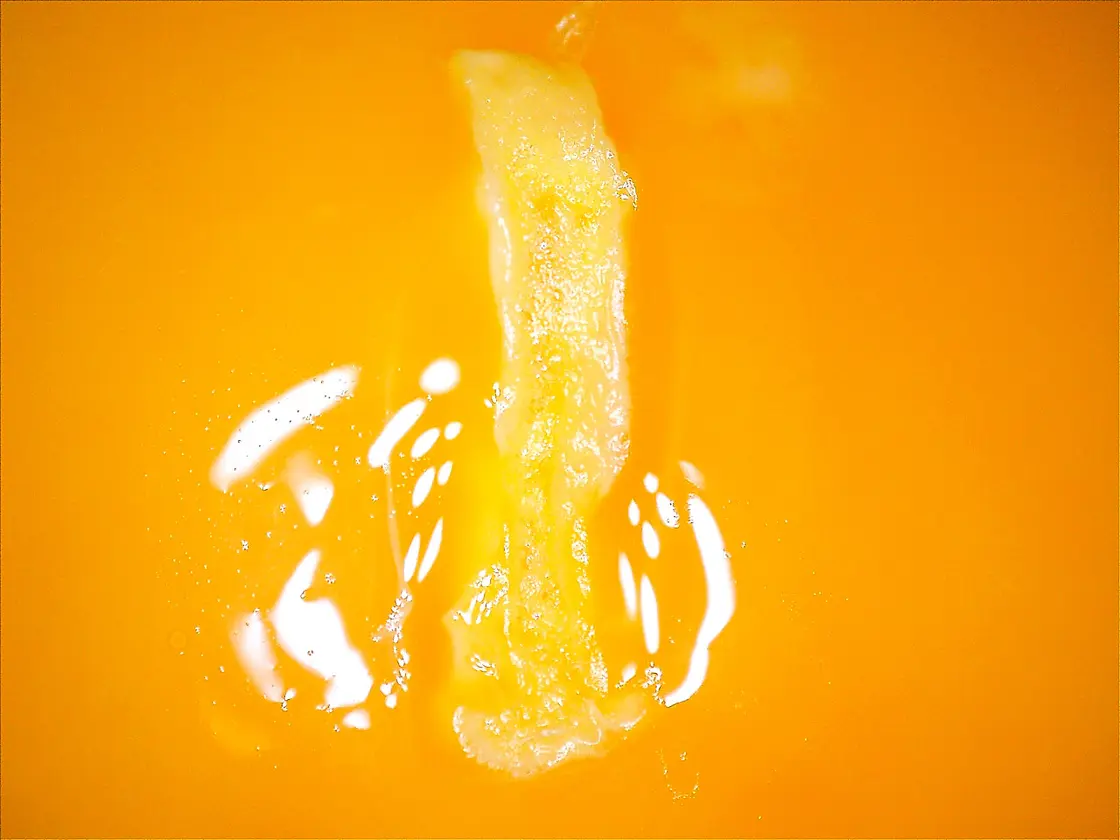

Conventional High Frequency Generator
An example of poor shape of coagulation,
poor edge sharpness and poor homogeneity
Fig. 4
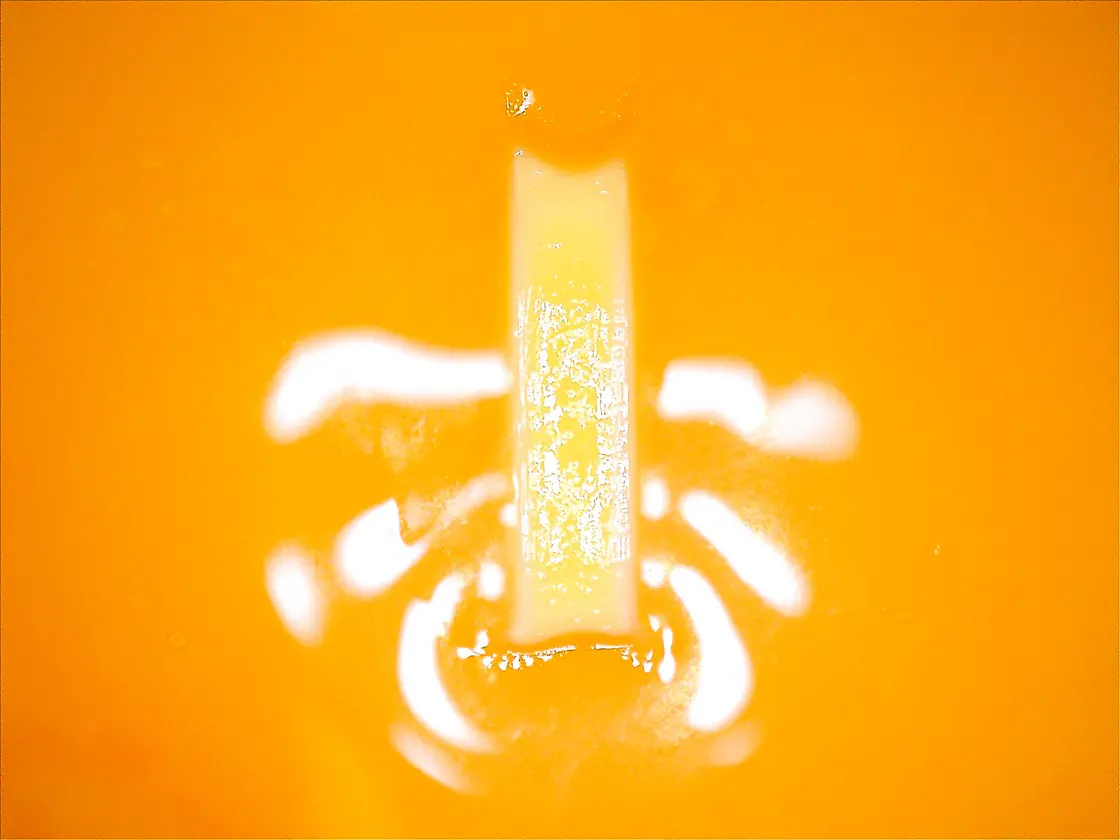

CURIS 4 MHz Radiofrequency Generator
An example of good shape of coagulation,
good edge sharpness and good homogeneity
Fig. 5
The evaluations revealed a clear difference between the two generators. Overall, the impedance-controlled CURIS© 4 MHz radiofrequency generator produced better results in terms of edge sharpness, homogeneity and shape of coagulation compared to conventional high frequency. The coagulations produced by the CURIS© 4 MHz radiofrequency generator were evaluated in excellent range whereas the coagulations produced by the conventional high frequency generator were much less favorable (see fig. 7-9). Since all three criteria achieved better results using 4 MHz radiofrequency technology, it can be concluded that the impedance-controlled CURIS© 4 MHz radiofrequency generator leads to gentler tissue effects.9
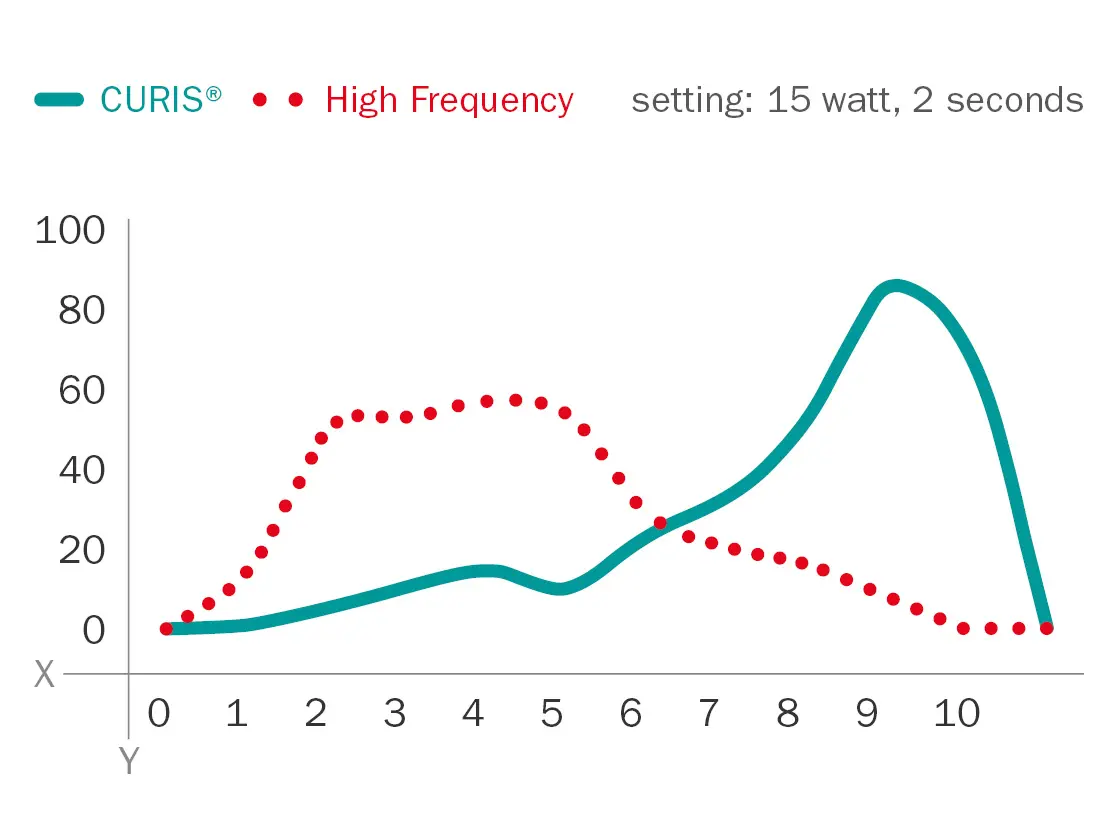
Edge sharpness of coagulations at 2 seconds activation time
Fig. 6
X: Evaluation on a visual analog scale from 0 (“very poor”) to 10 (“excellent”)
Y: Number of evaluations
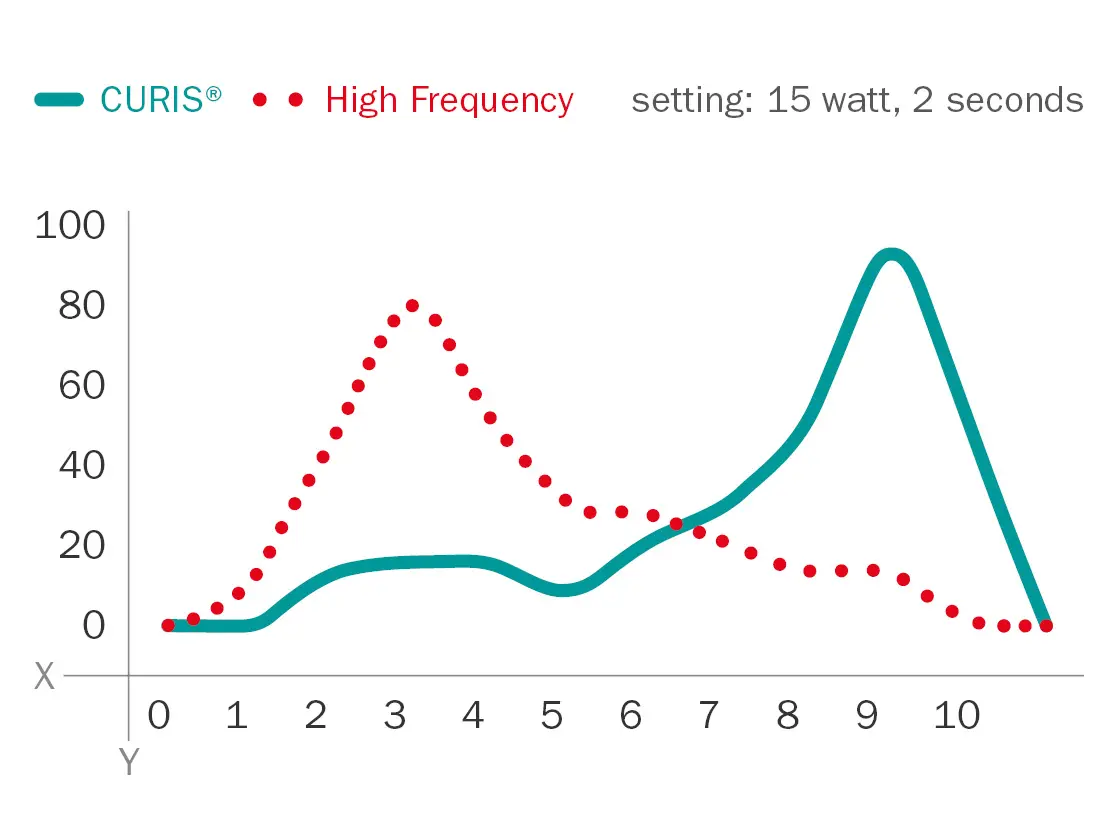
Homogeneity of coagulations at 2 seconds activation time
Fig. 7
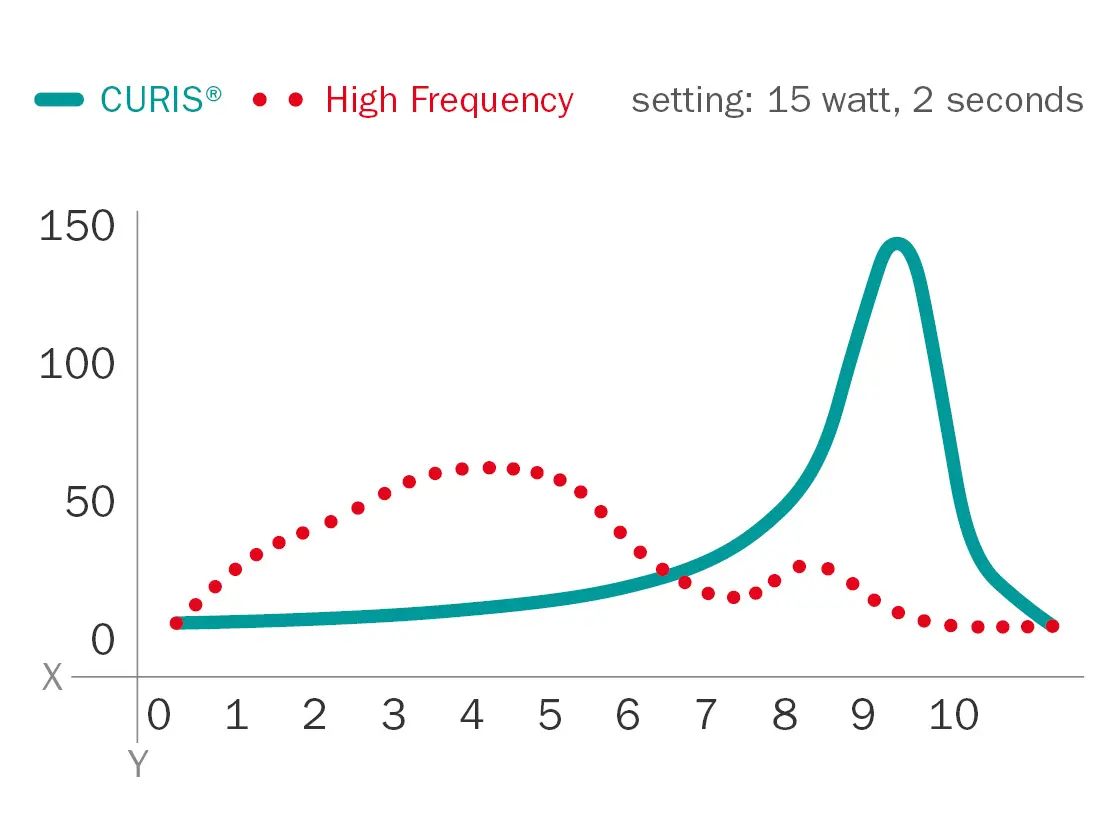
Shape of coagulation at 2 seconds activation time
Fig. 8
Discover the right solution for your specialty
Whether you’re making precise cuts or achieving reliable coagulation, our 4 MHz radiofrequency generators provide maximum control while minimizing thermal damage.
References
1 Bran, G M et al. Bipolar Radiofrequency Volumetric Tissue Reduction of Inferior Turbinates: Evaluation of Short-Term Efficacy in a Prospective, Randomized, Single-Blinded, Placebo-
Controlled Crossover Trial. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2012.
2 Neumann, K et al. Behandlung der kindlichen symptomatischen Tonsillenhyperplasie - Radiofrequenztonsillotomie als Mittel der
Wahl. HNO-Abstractband, Dt HNO-Kongress München, 2009, p. 186.
3 Pang, K P Siow, J K. Sutter Bipolar Radiofrequency Volumetric Tissue Reduction of Palate for Snoring and Mild Obstructive
Sleep Apnoea: Is One Treatment Adequate? J Laryngology and Otology, V 123, 2009, p. 750-754.
4 Hoffmann TK et al. Comparative analysis of resection tools suited for transoral robot-assisted
surgery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2014; 271:1207-13.
5 Hofauer B et al. Radiofrequency in Oral and oropharyngeal tumor surgery. Auris Nasur Larynx, 2020; 47(1):148 - 153.
6 Muehlfay G et al. A study of the type of lesions achieved by three electrosurgical methods and their way of healing. Rom J Morphol Embryol, 2015.
7 Vogt K et al. Comparison of the thermal effects of Coblation and Radiofrequency waves in a porcine turbinate model. Romanian Journal of Rhinology, 2018.
8 Holder, D S “Brief introduction to Bioimpedance” in: Electrical Impedance Tomography–Methods, History and Applications. IOP Publishing Ltd 2005.
9 Sutter Medizintechnik, data on file, 2019.
10 Sutter Medizintechnik, data on file, 2020.
11 Basterra J et al. Transoral Resection of Supraglottic Tumors Using Microelectrodes (54 Cases) EUR Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2014; 271 (9): 2497-502.










